Digesting food can take anywhere from 24 to 72 hours, but it varies depending on what you eat. Simple carbs like pasta pass through quickly (30-60 minutes in your stomach), while protein and fat (meat, fish) take much longer (2-4 hours in your stomach).
After your stomach, food spends 2-6 hours in the small intestine and then 10-59 hours in the large intestine for further breakdown. Factors like your age, metabolism, and activity level also influence digestion speed.
How Long Does It Take To Digest Food?
Have you ever wondered how long it takes for the food you eat to be fully digested? The journey of digestion is a complex process that involves various stages and factors influencing the time it takes for your body to break down and absorb nutrients from the food you consume.
The Digestive Process: An Overview
The digestive process begins in the mouth, where enzymes in saliva start breaking down carbohydrates. As food travels through the esophagus to the stomach, stomach muscles churn and mix it with gastric juices containing hydrochloric acid and enzymes. From there, partially digested food moves to the small intestine, where further breakdown and absorption of nutrients occur. Finally, undigested material passes into the large intestine for water absorption before being eliminated as waste.
Factors Affecting Digestion Time
Several factors can influence how long it takes for food to be digested. Age, gender, metabolism, stress levels, and hydration all play a role in digestion speed. For instance, younger individuals tend to have faster digestion rates compared to older adults, while stress can slow down the digestive process.
Digestion Time for Different Types of Food
Proteins, fats, and carbohydrates are digested at different rates. Proteins typically take 3-4 hours to digest, fats can take 6-8 hours, and carbohydrates are usually processed within 2-3 hours. Fiber-rich foods can help regulate digestion by slowing down the absorption of nutrients.
Digestive Disorders and Their Impact on Digestion Time
Digestive disorders such as GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), IBS (irritable bowel syndrome), or celiac disease can significantly affect digestion time. These conditions may lead to symptoms like bloating, indigestion, or diarrhea, altering the normal digestive process.
Tips for Improving Digestion
Improving digestion involves adopting healthy habits such as chewing food thoroughly, staying hydrated, and consuming a nutrient-rich diet. Including probiotics and digestive enzymes in your meals can also aid in better digestion and nutrient absorption.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Persistent digestive issues like severe abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, or blood in stool should not be ignored. Consulting a gastroenterologist for proper evaluation and diagnostic tests is crucial to identify underlying health conditions affecting digestion.
How Does Digestion Work?
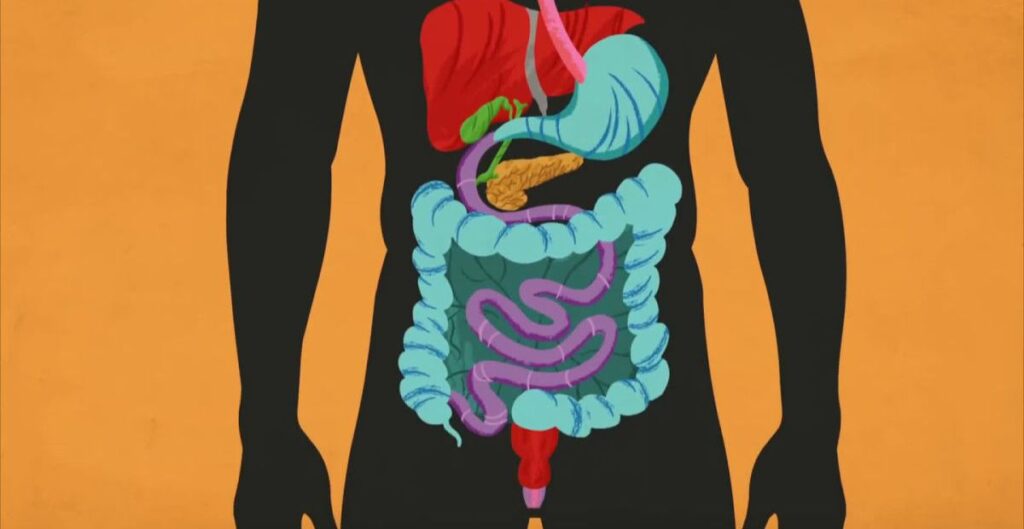
Understanding how digestion works is essential for maintaining optimal health. The digestive system is a complex network of organs working together to break down food into nutrients that our bodies can use for energy and growth.
Digestive Conditions
Various health conditions can impact digestion, leading to discomfort and complications. Conditions like acid reflux, Crohn’s disease, or lactose intolerance can disrupt the normal digestive process, requiring medical intervention and dietary modifications.
How To Improve Digestion
Improving digestion involves making lifestyle changes such as eating slowly, avoiding overeating, and incorporating fiber-rich foods in your diet. Regular physical activity and stress management techniques can also support healthy digestion.
Factors That Influence How Long Food Stays In Your Stomach
The composition of your meals plays a significant role in determining how long food stays in your stomach. High-fat foods tend to linger longer in the digestive tract compared to high-fiber or protein-rich foods. Individual factors like age, metabolism, and overall health also influence gastric emptying time.
What Foods Are Best For Digestion?
Foods That Slow Digestion
- High-fat foods like fried dishes
- Processed foods with added sugars
- Red meat and dairy products
Foods That Speed Up Digestion
- Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains like oats and quinoa
- Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and kefir
Incorporating a balanced diet with a variety of nutrient-dense foods can support healthy digestion and overall well-being. Making conscious choices about what you eat and how you eat can positively impact your digestive health in the long run.
Remember, taking care of your digestive system through proper nutrition, hydration, and lifestyle choices is key to maintaining good health. Listen to your body’s signals, seek medical attention when needed, and make informed decisions about your diet to support optimal digestion. Your gut health plays a crucial role in your overall well-being – nurture it wisely.
People Also Ask (FAQ’s)
Does it take 30 minutes to digest food?
Digestion time varies depending on the type of food, but generally, it takes longer than 30 minutes for food to fully digest.
How long does it take for your stomach to empty after eating?
It typically takes 2 to 4 hours for the stomach to empty after a meal, but this can vary based on individual factors and the composition of the meal.
Is 2 hours enough to digest food?
Two hours may not be enough time for complete digestion, especially for larger meals or foods that are high in fat or fiber.
How long does it take to fully digest food and poop it out?
The process of digestion and elimination can take anywhere from 24 to 72 hours, depending on the individual and the specific food.
Why am I pooping out food I ate 6 hours ago?
Rapid transit time can occur due to factors like digestive issues, certain foods, or a fast metabolism, leading to food appearing in the stool relatively quickly after eating.
Final Words
Your digestive journey can take anywhere from 1 to 3 days! It depends on what you eat. Sugary foods zip through quickly, while protein and fat take much longer to break down. After your stomach (1-4 hours), food spends additional hours in the small intestine and large intestine for final processing.

